
Trichomoniasis

trichomoniasis(or “trich”) is a very common sexually transmitted disease (STD). It is caused by infection with a protozoan parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. Although symptoms of the disease vary, most people who have the parasite cannot tell they are infected.
How common is trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis is the most common curable STD. In the United States, an estimated 3.7 million people have the infection. However, only about 30% develop any symptoms of trichomoniasis. Infection is more common in women than in men. Older women are more likely than younger women to have been infected with trichomoniasis.
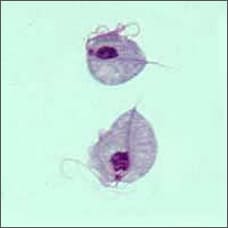 Two Trichomonas vaginalis parasites, magnified (seen under a microscope)
Two Trichomonas vaginalis parasites, magnified (seen under a microscope)
How do people get trichomoniasis?
The parasite passes from an infected person to an uninfected person during sex. In women, the most commonly infected part of the body is the lower genital tract (vulva, vagina, cervix, or urethra). In men, the most commonly infected body part is the inside of the penis (urethra). During sex, the parasite usually spreads from a penis to a vagina, or from a vagina to a penis. It can also spread from a vagina to another vagina. It is not common for the parasite to infect other body parts, like the hands, mouth, or anus. It is unclear why some people with the infection get symptoms while others do not. It probably depends on factors like a person’s age and overall health. Infected people without symptoms can still pass the infection on to others.
What are the signs and symptoms of trichomoniasis?
About 70% of infected people do not have any signs or symptoms. When trichomoniasis does cause symptoms, they can range from mild irritation to severe inflammation. Some people with symptoms get them within 5 to 28 days after being infected. Others do not develop symptoms until much later. Symptoms can come and go.
Men with trichomoniasis may notice:
- Itching or irritation inside the penis;
- Burning after urination or ejaculation;
- Discharge from the penis.
Women with trichomoniasis may notice:
- Itching, burning, redness or soreness of the genitals;
- Discomfort with urination;
- A change in their vaginal discharge (i.e., thin discharge or increased volume) that can be clear, white, yellowish, or greenish with an unusual fishy smell.
Having trichomoniasis can make it feel unpleasant to have sex. Without treatment, the infection can last for months or even years.
What are the complications of trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis can increase the risk of getting or spreading other sexually transmitted infections. For example, trichomoniasis can cause genital inflammation that makes it easier to get infected with HIV, or to pass the HIV virus on to a sex partner.
How does trichomoniasis affect a pregnant woman and her baby?
Pregnant women with trichomoniasis are more likely to have their babies too early (preterm delivery). Also, babies born to infected mothers are more likely to have a low birth weight (less than 5.5 pounds).
How is trichomoniasis diagnosed?
It is not possible to diagnose trichomoniasis based on symptoms alone. For both men and women, your health care provider can examine you and get a laboratory test to diagnose trichomoniasis.
What is the treatment for trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis can be treated with medication (either metronidazole or tinidazole). These pills are taken by mouth. It is safe for pregnant women to take this medication. It is not recommended to drink alcohol within 24 hours after taking this medication.
People who have been treated for trichomoniasis can get it again. About 1 in 5 people get infected again within 3 months after receiving treatment. To avoid getting reinfected, all sex partners should get treated with antibiotics at the same time. Wait to have sex again until everyone has been treated and any symptoms go away (usually about a week). Get checked at 3 months to make sure you have not been infected again, or sooner if your symptoms come back before then.
How can trichomoniasis be prevented?
The only way to avoid STDs is to not have vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
If you are sexually active, you can do the following things to lower your chances of getting trichomoniasis:
- Be in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who has been tested and has negative STD test results;
- Use latex condoms the right way every time you have sex. This can lower your chances of getting trichomoniasis.
Another approach is to talk about the potential risk of STDs before you have sex with a new partner. That way you can make informed choices about the level of risk you are comfortable taking with your sex life.
If you or someone you know has questions about trichomoniasis or any other STD, talk to a health care provider.
